In 2022, between mid-March and early April, Equifax, one of the major credit reporting agencies, issued credit reports for approximately 300,000 individuals that were off by around 20 points, enough to impact loan decisions and interest rates. Although the company initially attributed the error to ‘coding errors due to a legacy on-prem server’, it was enough to pull down their stock price by 5%, resulting in a class action lawsuit. While publicly acknowledging the error, the company promised to ‘accelerate the migration of data to the more secure Equifax cloud to provide additional control… And prevent such incidents in the future.’
According to the MIT Sloan Management Review, the cost of bad data can lead to a revenue erosion of anywhere between 15% and 25% for retail companies in the US. If you find this astonishing, IBM estimates the annual impact of bad data at nearly US$3.1 trillion, roughly equivalent to the combined GDP of the UK, France, and India.
In investing and business, data is rarely perfect—financial statements may contain reporting quirks, customer surveys are biased, and satellite images have noise. Yet, businesses like hedge funds, retailers and many other thrive by sifting through massive, messy datasets—shipping logs, credit card swipes, even weather data—to uncover signals. While quality ensures reliability, too much filtering can strip away valuable patterns. Conversely, sheer quantity can offset imperfections by amplifying signal-to-noise ratios. The trade-off is not binary; the real edge lies in balancing volume with rigorous preprocessing, extracting insights from “imperfect” data that competitors overlook.
Companies today rely on a broad range of data sources—from CRM logs and IoT sensors to satellite imagery and social media sentiment. However, even a small pocket of bad data in a single dataset can trigger outsized consequences. For example, in 2012 JPMorgan’s “London Whale” trading loss was partly blamed on faulty risk modeling data. Now, imagine the quantum of business loss when errors creep across dozens of interconnected datasets. The impact compounds—mispricing products, misallocating capital, or missing critical market signals—turning poor data hygiene into a systemic business risk.
Cost of Poor Data Quality
- $12.9 million is the average annual financial loss organizations face due to poor data quality, according to Gartner research.
- Bad data can cause an average 12% loss in revenue for companies, as found in an Experian study cited by Intelligent Data Solutions.
- Over 40% of marketing or operational budgets are wasted on repeated work, corrections, or poor targeting stemming from bad data quality.
- Employees spend up to 20-27% of their productivity time dealing with inaccurate or incomplete data, lowering overall efficiency.
- Improving data quality can drive a 15–25% increase in sales, supported by studies showing enhanced lead quality and conversion rates from better data hygiene.
- Research has shown that approximately 47% of newly created data records contain at least one critical error that could impact work.
- According to a Linkedin user, on average, 20% of database records are considered “dirty” or contain data quality issues, emphasizing the prevalence of flawed data in enterprise systems.
What is Bad Data?
Before diving into the costs, let’s define our adversary. “Bad data” encompasses a range of imperfections:
- Inaccurate: Incorrect information (e.g., wrong address, misspelled name).
- Incomplete: Missing critical fields (e.g., phone number, email address).
- Inconsistent: Variations in format or spelling across different systems (e.g., “New York,” “NY,” “N.Y.”).
- Outdated: Information that is no longer current (e.g., former employee details, old pricing).
- Duplicate: Multiple records for the same entity (e.g., a customer listed twice).
- Irrelevant: Data that serves no purpose for current business objectives.
Any of these flaws can contaminate your data ecosystem, leading to a cascade of negative consequences. Contrary to popular belief, bad data is the norm in most environments, which has led to the creation of ‘data cleansing’ and ‘data enrichment’ tools, which act as a screen to ensure that the data that comes into the system can be cleaned up and enriched using applications and tools. And while everyone has heard of terms like ‘garbage in, garbage out’ and truisms like ‘a decision is only as good as the data it is based on’, businesses spend an enormous amount of time, money, and risk their reputations on decisions based on data that is purported to be clean and accurate.
Bad data isn’t just a nuisance; it’s a fundamental flaw that can undermine even the most sophisticated strategies. It’s ‘hidden’ because its impact often manifests indirectly, slowly eroding profitability, damaging reputation, and stifling innovation without a clear line item on a balance sheet. Understanding these hidden costs is the first step toward recognizing the urgent need for robust data quality initiatives.
Unlike a factory shop-floor error, the actual danger of bad data lies in its indirect and pervasive impact across various facets of an organization. The effect is not realized until the event occurs, and businesses are disrupted by a real-life situation. Some of the apparent effects lead to:
- Financial Costs: The Leaking Bucket
- Lost Revenue and Missed Opportunities: Inaccurate customer data can lead to failed marketing campaigns, misdirected sales efforts, and missed cross-selling or upselling opportunities. In Q1 2022, Unity Technologies experienced a significant data quality issue when its Audience Pinpoint tool ingested inaccurate data from a large customer. This corrupted the training sets for its machine learning algorithms, impairing ad targeting and campaign performance. The incident directly impacted Unity’s revenue-sharing model, resulting in an estimated $110 million loss.
- Operational Inefficiencies and Rework: Bad data causes delays, rework, and increased operational costs. Imagine a supply chain disrupted by incorrect inventory figures, your employees will spend valuable time validating, correcting, or working around faulty information instead of focusing on productive tasks.
- Increased Marketing and Sales Spend: Sales teams waste cycles on prospects with inaccurate profiles, increasing their cost of acquisition.
- Compliance Fines and Legal Issues: In regulated industries, inaccurate or non-compliant data can lead to hefty fines and legal repercussions. Data privacy regulations (like GDPR or CCPA) mandate data accuracy; non-compliance can be incredibly costly.
- Reputational Costs: Eroding Trust
- Damaged Customer Trust: Nothing erodes customer trust faster than receiving irrelevant communications, having one’s name misspelled repeatedly, or being asked for information that has already been provided. This leads to frustration, churn, and negative word of mouth.
- Erosion of Brand Image: A company consistently making mistakes due to bad data (e.g., incorrect invoices, delayed deliveries) projects an image of incompetence and unreliability, severely damaging its brand reputation in the market.
- Poor Decision-Making Leading to Public Failures: If strategic decisions are based on flawed market research or inaccurate customer segmentation, the resulting product launches or business expansions can fail spectacularly, leading to public embarrassment and significant financial losses.
- Strategic Costs: Stifled Growth
- Inaccurate Insights and Flawed Business Decisions: This is perhaps the most dangerous hidden cost. If the data informing your strategic planning is flawed, your decisions will be too. You might invest in the wrong markets, target the wrong demographics, or misallocate resources, leading to suboptimal outcomes and missed growth opportunities.
- Stifled Innovation: Data is the fuel for innovation. If your R&D or product development teams are working with incomplete or inconsistent data, their ability to identify trends, predict future needs, or develop truly innovative solutions is severely hampered.
- Reduced Competitive Advantage: Competitors with cleaner, more reliable data can make faster, more accurate decisions, respond to market changes more effectively, and personalize customer experiences more precisely, leaving you behind.
- Employee Morale and Frustration: Constantly battling bad data leads to frustration, reduced productivity, and potentially higher turnover as talented individuals seek more efficient working environments
The solution is not rocket science. It simply means that you must have the discipline to create a process and ensure it is implemented without anyone taking shortcuts. The problem is not technical, but rather more to do with process, discipline, culture, and training: things that every workflow demands as de rigueur. For instance:
- Create a data governance framework with clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and accountability. Leverage platforms that offer automated deduplication, validation, and enrichment, and break down silos by integrating disparate systems to give you a single source of truth. Data lakes or cloud-based data warehouses help centralize and synchronize data for unified access and analysis.
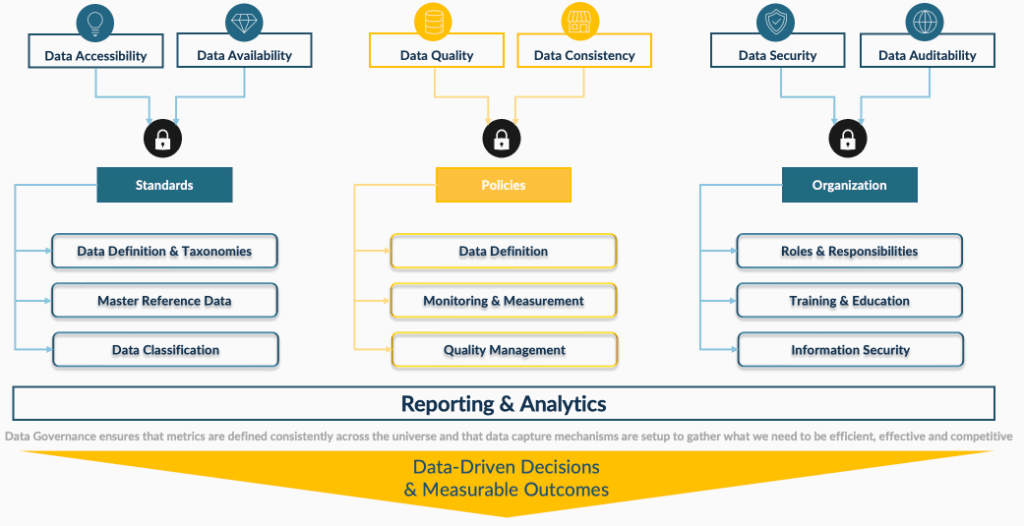
Data Governance is a must-have because accuracy in analytics and AI is worth striving for.
- Conduct regular data audits: Establish recurring cycles to clean and refresh databases, especially customer and vendor records. This is particularly critical in fast-growing markets like India, where mobile numbers, addresses, and email IDs are frequently updated. Data audits make all the hard work of data collection count by ensuring the output is meaningful, not just data for the sake of data.
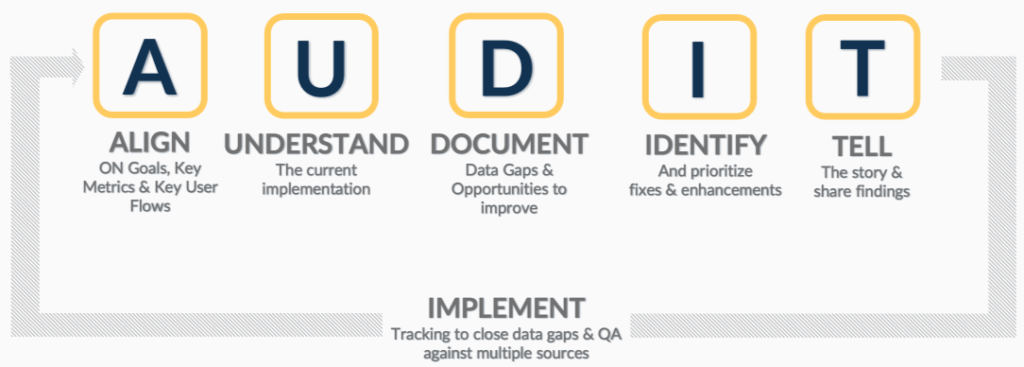
You can’t imagine what you can’t measure!
- Empower your employees with data literacy training. Help them understand how their inputs affect downstream processes and outcomes. The cultural shift toward viewing data as a strategic asset can only happen when people at every level are aligned.
- Establish key data quality KPIs, such as completeness, accuracy, timeliness, and consistency, and track them over time. Dashboards can make this visible and actionable for decision-makers.
Ignoring bad data is like building a skyscraper on a shaky foundation – eventually, it will crumble. By proactively investing in data quality, establishing transparent governance, and fostering a data-aware culture, CEOs can transform data from a hidden liability into their most valuable strategic asset. In today’s business environment, good data has to become a hygiene factor for a business to thrive.
By Priyanka Baram
